泛型
泛型是什么?
泛型(Generics) 是C#中的类型参数化技术,允许编写可处理多种数据类型的代码,避免为每种类型重复编写逻辑。
核心思想:用占位符T表示类型,使用时再指定具体类型。
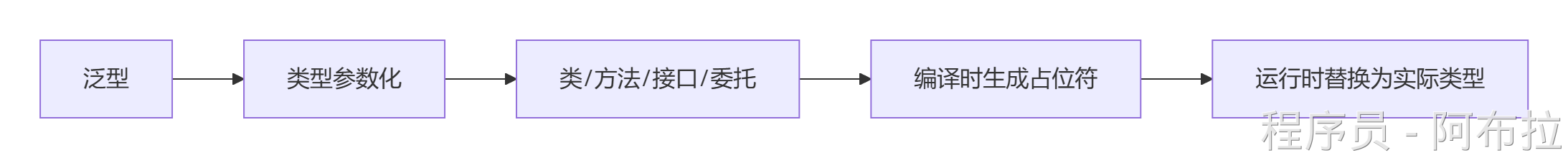
示例对比:
// 非泛型:只能处理int类型
public class IntList {
private int[] items;
}
// 泛型:可处理任意类型
public class List<T> {
private T[] items; // T是类型占位符
}
💡 当调用List<int>时,编译器将T替换为int,生成专用类。
泛型的核心类型
(1) 泛型类
public class Box<T> {
private T _value;
public void SetValue(T value) => _value = value;
public T GetValue() => _value;
}
// 使用
var intBox = new Box<int>();
intBox.SetValue(123);
一个类可支持多种类型参数,如Dictionary<TKey, TValue>。
(2) 泛型方法
public static T Max<T>(T a, T b) where T : IComparable<T> {
return a.CompareTo(b) > 0 ? a : b;
}
// 调用(类型自动推断)
int max = Max(10, 20); // T被推断为int
即使非泛型类中也可定义泛型方法。
(3) 泛型接口
public interface IRepository<T> {
void Add(T entity);
T GetById(int id);
}
public class UserRepository : IRepository<User> {
// 实现接口方法
}
接口契约可复用,实现类指定具体类型。
泛型约束
约束确保类型参数符合要求,提升安全性
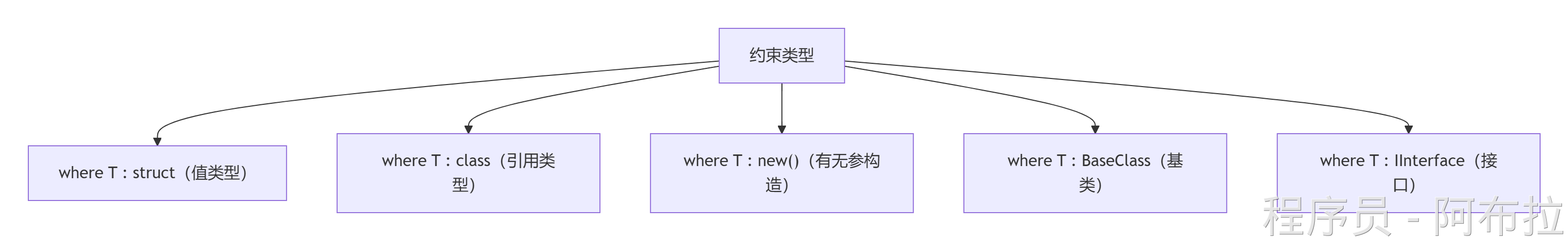
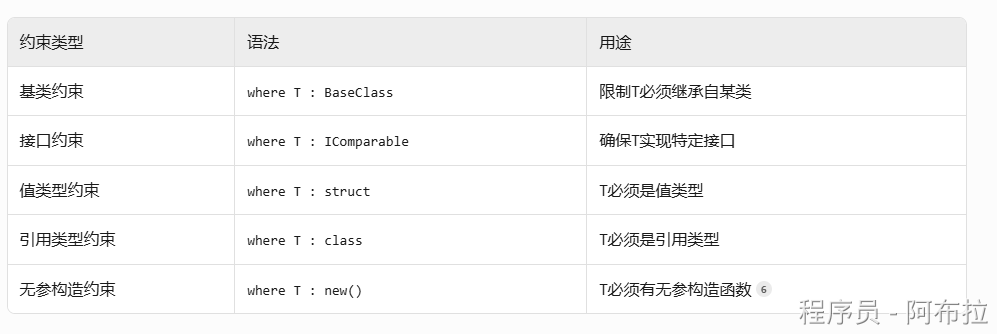
示例
public class DataProcessor<T> where T : class, IEntity, new() {
public void Process() {
var obj = new T(); // 安全创建实例
obj.Id = 1; // 可访问IEntity成员
}
}
若无约束,new T()或obj.Id会编译报错。
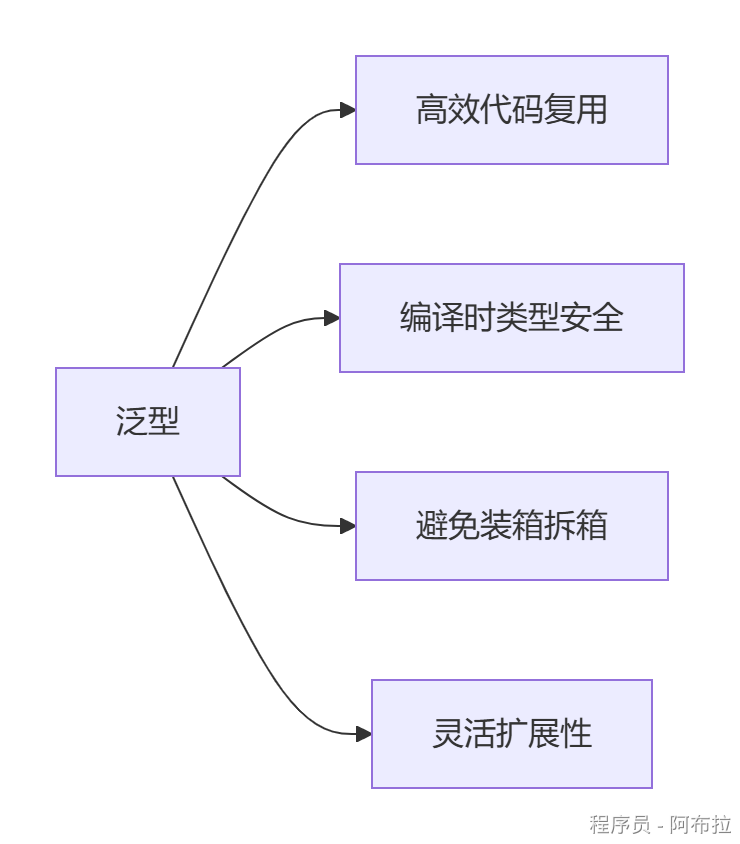
泛型核心优势
| 优势 | 说明 | 示例对比 |
|---|---|---|
| 类型安全 | 编译时检查类型错误,避免运行时异常 | List<int>添加字符串会报错 vs ArrayList添加任意类型导致运行时错误 |
| 性能优化 | 避免值类型的装箱/拆箱操作 | List<int>直接操作栈内存,ArrayList需装箱到堆 |
| 代码复用 | 一套逻辑处理多种类型 | Max<T>方法支持int/string/double等 |
| 可读性 | 代码意图明确,减少类型转换噪音 | Dictionary<string, User> vs Hashtable |
实际应用场景
(1) 集合类(最常用)
List<int> numbers = new List<int>(); // 动态数组
Dictionary<string, User> userCache; // 键值对
Queue<Order> orderQueue; // 先进先出
优先使用泛型集合而非ArrayList/Hashtable。
(2) 泛型缓存
public static class Cache<T> {
static Cache() {
// 每个T类型生成独立缓存
}
public static T Get(string key) { ... }
}
比字典缓存更快,因类型信息在编译时确定。
(3) 工厂模式
public class Factory<T> where T : new() {
public T Create() => new T();
}
var userFactory = new Factory<User>();
User user = userFactory.Create();
约束new()确保可实例化。
高级特性:协变与逆变
- 协变(out):子类泛型→父类泛型(安全)
IEnumerable<Dog> dogs = new List<Dog>();
IEnumerable<Animal> animals = dogs; // 合法
- 逆变(in):父类泛型→子类泛型(需谨慎)
Action<Animal> feedAnimal = a => a.Feed();
Action<Dog> feedDog = feedAnimal; // 合法
仅适用于接口/委托,通过out/in关键字实现。